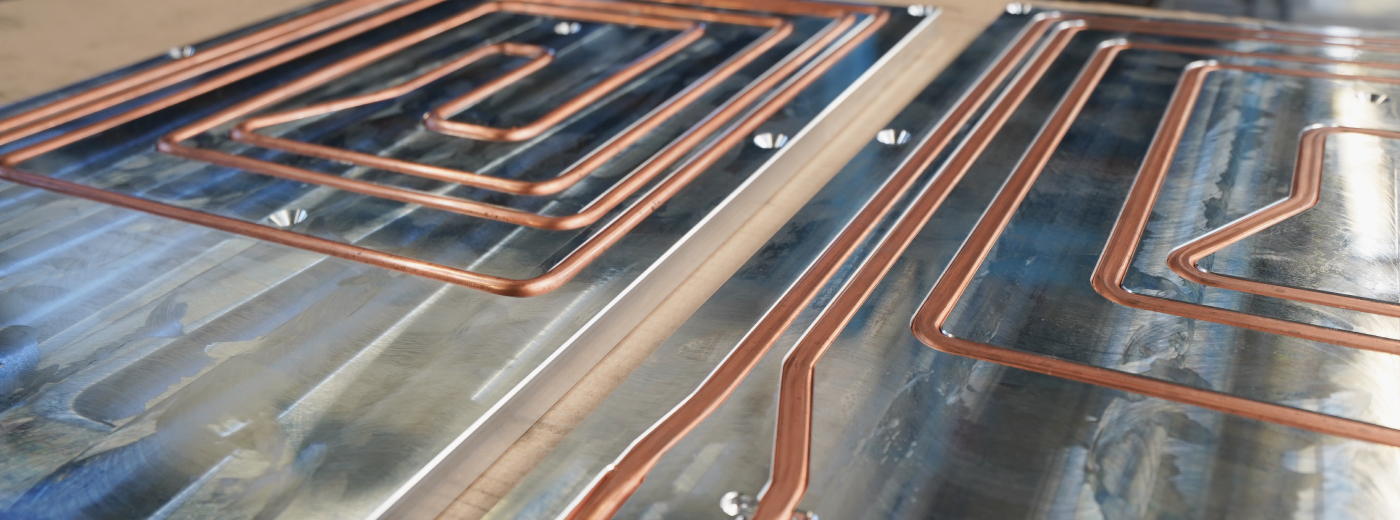

Pressing
Learn how modern pressing technologies enable highly efficient heat sinks for electronics and liquid cooling – precise, efficient, and application-optimized.
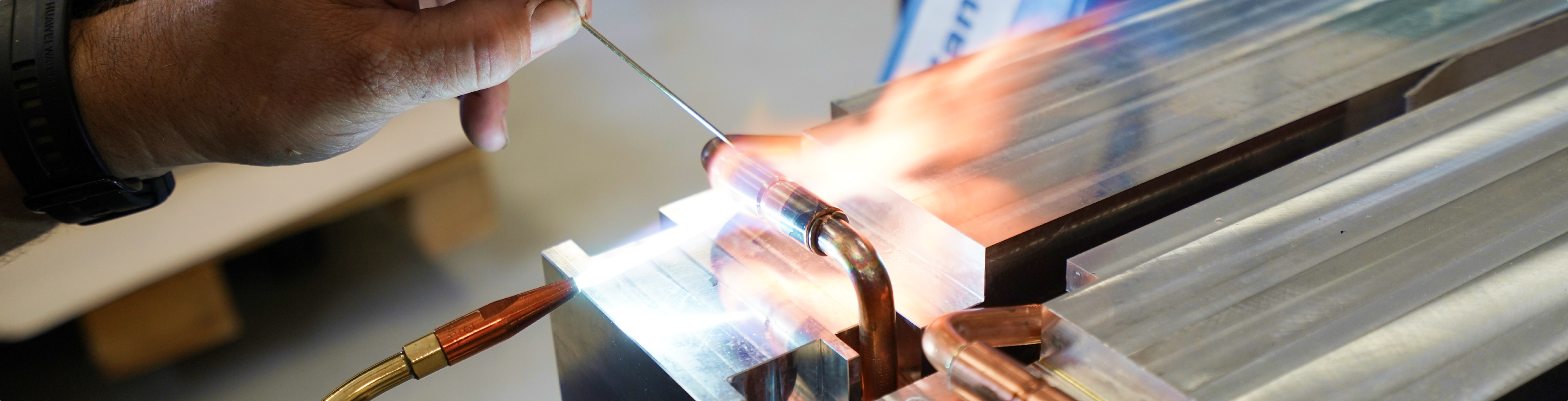
Soldering relies on precise and reliable joining techniques. Whether hard soldering, soft soldering, induction soldering, resistance soldering, or vacuum soldering – each method allows the accurate integration of tube and component structures into heat sinks and liquid cooling plates. The metallic bond between the components provides efficient thermal conductivity, high mechanical stability, and long-lasting cooling performance, even for complex geometries or high-performance applications.
Learn more in a conversationDepending on the requirements, different soldering methods are used, each offering specific advantages. From traditional flame soldering to induction soldering, resistance soldering, and vacuum soldering, these technologies enable precise joining of tube and component structures. They ensure efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical stability, and long-lasting cooling – even for complex geometries or high-performance applications.
Flame soldering uses an open flame to melt solder material between components. There is soft soldering (below 450 °C, e.g., for copper/aluminum) and hard soldering (above 450 °C, e.g., for stainless steel or copper alloys).
Benefits:
Soft soldering: low thermal stress
Hard soldering: very strong and durable joints
Suitable for various material types
Flexible in temperature and application
Induction soldering generates heat through electromagnetic induction. A coil produces a magnetic field that induces eddy currents in the components, locally heating the surface.
Benefits:
Precise and localized heating
Fast soldering connections
Contactless heating – gentle on sensitive parts
Selective heating possible
In resistance soldering, electric current is passed through the material. The electrical resistance of the material generates the heat that melts the solder.
Benefits:
Precise control of heat input
Fast heating of the solder area
Ideal for small to medium-sized components
Good temperature control for repeatable soldering
Vacuum soldering is performed under reduced pressure, which lowers the boiling point of the solder. This allows soldering at lower temperatures and reduces oxide formation.
Benefits:
High-quality solder joints without oxidation
Soldering at lower temperatures
No flux required
Precise control of the soldering process
Our team of experts provides fast, practical, and tailored advice – for precise joints, efficient heat dissipation, and long-lasting results.