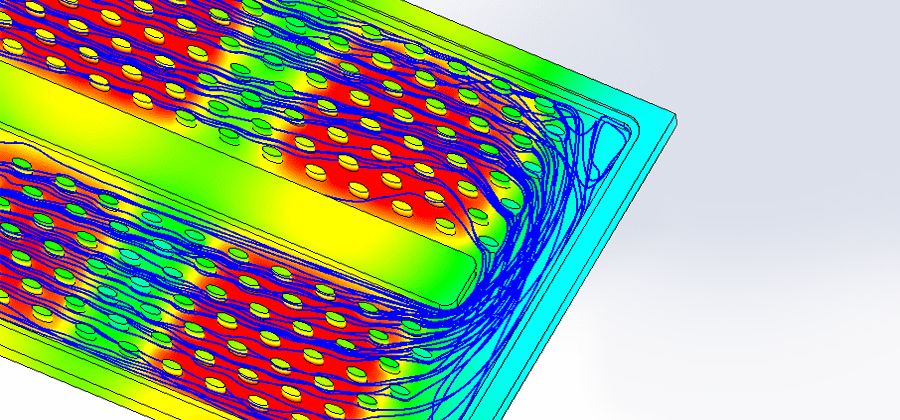
Developing Heat Sinks Using Thermal Simulations
Published: 10.01.2023
The development and optimization of cooling solutions can be carried out through two different methods:
Author: Benedikt Lausberg
Transistors are undoubtedly a central component of modern electronic circuits. They are used in many applications, from simple circuits to complex amplifiers. In this article, we will examine how transistors work, explore different types of transistors, consider their applications, and discuss how they can and should be cooled effectively.
How Transistors Work
A transistor is an electronic component made from semiconductors such as silicon or germanium. Its fundamental operation is based on controlling the flow of electrical current through the semiconductor.
There are two basic types of transistors: bipolar transistors and field-effect transistors (FETs).
Bipolar Transistors
Bipolar transistors have three terminals: the emitter, base, and collector. The current flow between the emitter and collector is controlled by the current flow between the base and emitter.
When a current flows between the base and emitter, a stronger current flow between the emitter and collector is enabled, a phenomenon known as transistor amplification.
Field-Effect Transistors (FETs)
Field-effect transistors also have three terminals: the source, gate, and drain. The current flow between the source and drain is controlled by the electric field generated by the gate.
When a voltage is applied to the gate, it creates an electric field within the semiconductor material, influencing the current flow between the source and drain. This effect is called the field effect.
Types of Transistors
There are various types of transistors, each with unique applications. Some of the most common types include:
Bipolar Transistors:
• NPN Transistor: Has a negatively charged emitter and a positively charged collector.
• PNP Transistor: Has a positively charged emitter and a negatively charged collector.
Field-Effect Transistors:
• MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor): Commonly used in high-frequency applications due to its efficiency.
• JFET (Junction Field-Effect Transistor): A simpler FET often used as an amplifier.
Applications of Transistors
• Amplifiers: Used in audio devices, radios, televisions, generators, and other electronic devices.
• Switches: Used as electronic switches in many applications.
Optimal Cooling of Transistors
Most transistor applications require effective cooling, as they can heat up under high power. Without proper cooling, heat can shorten the lifespan of the transistor or even cause malfunction. Various cooling methods include:
• Air Cooling: A simple and cost-effective method using a heat sink with fins or ribs to dissipate heat. Often paired with a fan for better airflow.
• Liquid Cooling: More efficient than air cooling. A liquid flows through pipes or internal channels to transfer heat away. It is more expensive but offers higher cooling capacity.
• Thermoelectric Cooling: Uses the Peltier effect. A Peltier element placed between the transistor and heat sink transfers heat away using electric current.
• Vacuum Cooling: Involves placing the transistor in a vacuum chamber with a cooling jacket for heat dissipation. Effective but costly.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right cooling method is critical for maintaining optimal performance and extending the lifespan of transistors. Poor cooling can lead to failures and costly replacements. Effective cooling not only enhances performance but also ensures the longevity and reliability of electronic systems.
© 2026 - Cool Tec Electronic GmbH